Table of Contents
ToggleThe Invisible Engine: What Keeps the Internet Running Non-Stop?
Let’s be honest. When you open Netflix at 11 PM on a Tuesday, or ask ChatGPT to help rewrite an email at dawn, you expect it to just work. We rarely stop to think about the massive physical infrastructure making that happen.
We like to talk about “the cloud,” as if our photos and emails are just floating around in the sky. But the reality is much heavier, hotter, and louder. “The cloud” is actually millions of physical servers housed in massive, fortress-like buildings called data centers.
These facilities are the engine rooms of the modern world. But here’s the kicker: engines usually need downtime for maintenance or refueling. So, how do data centers work 24/7 without ever hitting the pause button, especially now that demanding AI tools are hungrier than ever?
Let’s take a look inside these digital powerhouses to see how they pull off the impossible, every single second of the day.
It’s Not Just Computers; It’s the Infrastructure
If you walked into a modern data center, the first thing you’d notice is the noise—a constant, rushing hum of thousands of fans. You’d see endless rows of tall racks filled with blinking servers, connected by literal miles of fiber optic cables.
But the computers themselves are only half the story. The real magic of 24/7 uptime lies in the supporting infrastructure designed to ensure that absolutely nothing ever stops.
The secret word here is “Redundancy.” In plain English, redundancy means having a backup for everything. And often, a backup for the backup.
The Unstoppable Need for Power
Data centers are incredibly thirsty for electricity. With the recent boom in artificial intelligence, that thirst has turned into a drought. Powering AI infrastructure requires significantly more energy than running standard websites because AI chips (GPUs) run much hotter and work much harder.
Read our Article on:
Nvidia’s $1 Billion Bet on Nokia: Powering the AI-Native Future of 5G & 6G Networks
To ensure the lights never go out on your digital life, data centers use a multi-layered power strategy:
Multiple Grid Connections: They don’t just plug into one wall outlet. They often connect to totally different power utility substations. If one part of the city grid fails, the other takes over.
The UPS Bridge: What happens in the split second between the power going out and the backup kicking in? That’s where Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems come in. These are massive rooms filled with batteries that instantly take the load, ensuring your streaming video doesn’t even flicker.
Massive Backup Generators: If the outage lasts more than a minute, giant diesel or natural gas turbines roar to life. These backup generators for data centers can power the entire facility for days, as long as they have fuel.
Keeping Cool Under Extreme Pressure
Imagine how hot your laptop gets after an hour of gaming. Now, imagine tens of thousands of much more powerful computers crammed into one room, running at 100% capacity all day.
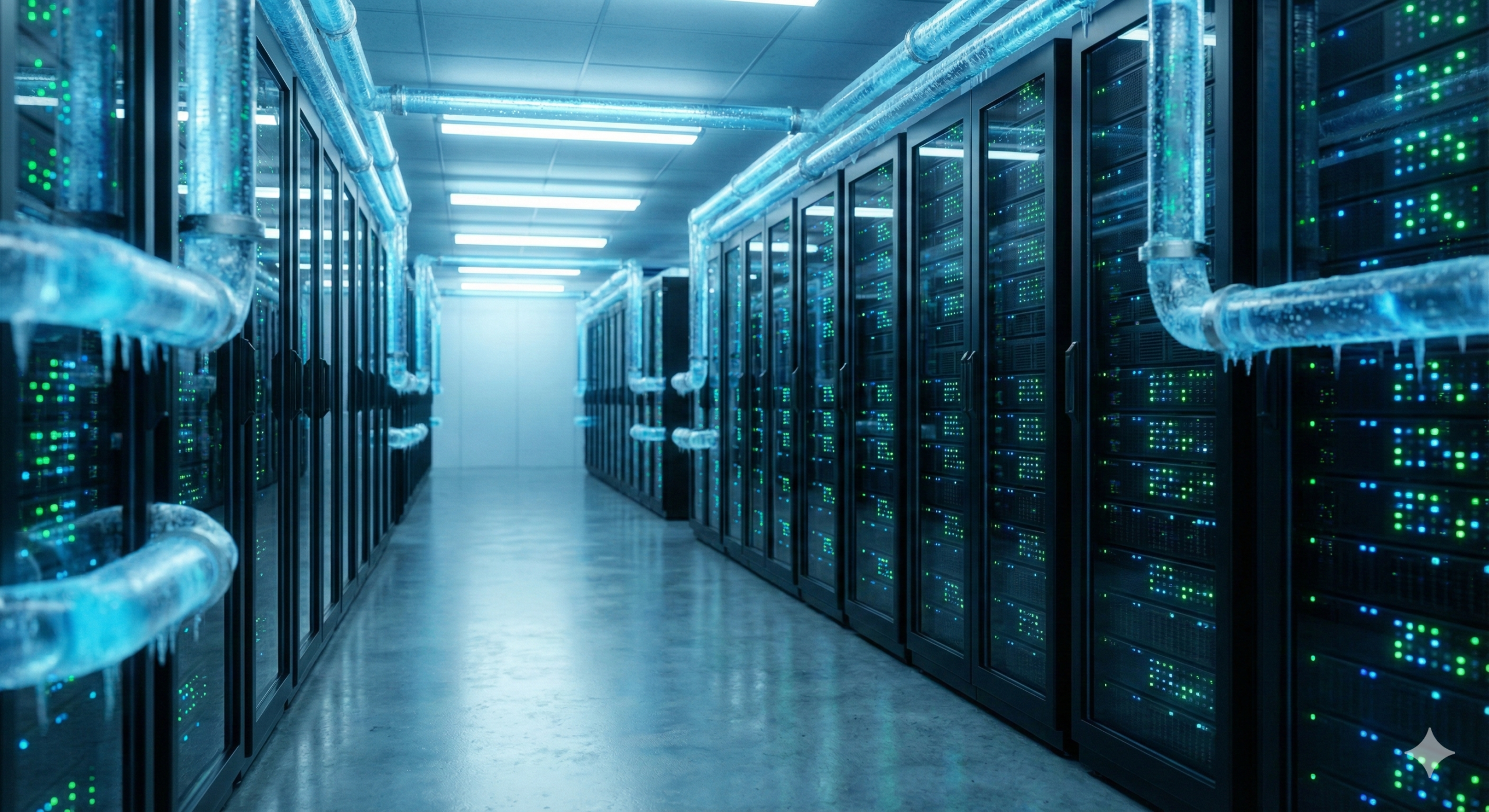

Without massive intervention, the equipment would melt down in minutes.
This is why data center cooling systems are just as critical as the power supply. Traditionally, this involved giant industrial air conditioners blasting cold air through raised floors.
However, the intense heat generated by modern AI processors is changing the game. Many cutting-edge facilities are now shifting to liquid cooling. This involves piping cool liquid directly over the hottest chips to pull heat away far more efficiently than air ever could. It’s like the difference between standing in front of a fan versus jumping into a cold pool on a hot day.
How AI Changed the Game
The demands of standard internet browsing versus training a massive AI model are vastly different. Here is a quick look at how the infrastructure has had to adapt.
| Feature | Traditional Data Center (Web/Email) | Modern AI Data Center |
| Primary Task | Storing files, serving web pages. | Complex calculations, training models. |
| Power Density | Moderate power needs per rack. | Extreme power needs per rack (hungry GPUs). |
| Cooling Needs | Standard air conditioning is usually fine. | Often requires advanced liquid cooling. |
| Location Focus | Near users for speed (latency). | Near cheap/abundant power sources. |
Read our Article on: N8N vs Zapier vs Make
Fort Knox for Your Data
When we think of data security, we usually think of hackers and firewalls. While cyber threats are real, physical threats are just as dangerous. You can’t have a 24/7 operation if someone can just walk in and unplug a server.
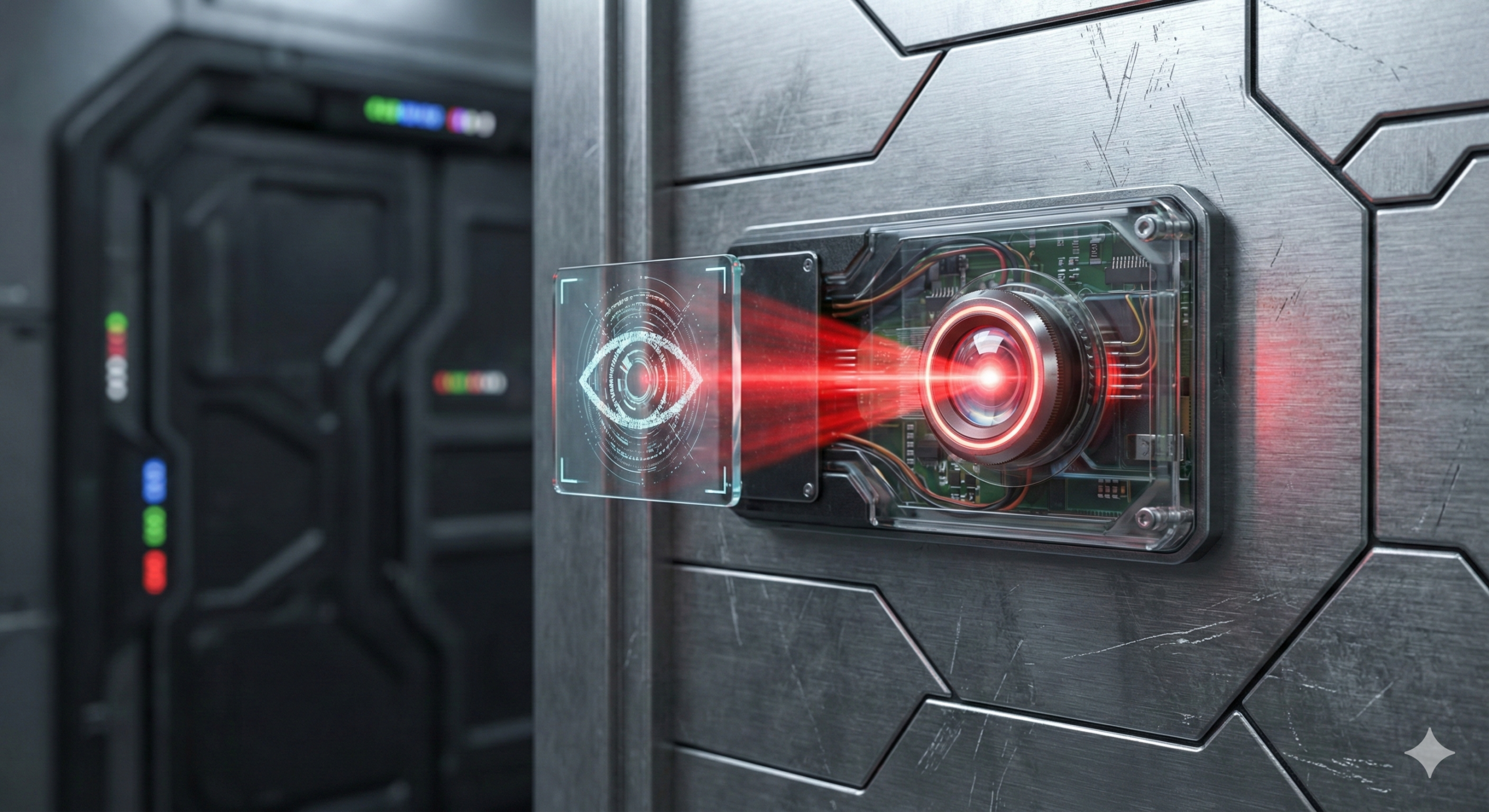
Physical data center security is intense. We are talking about facilities surrounded by crash-proof fences, manned by 24/7 security guards, and monitored by hundreds of cameras. Getting inside often requires passing through “man-traps” (secure airlocks) and using biometric scanners like fingerprint or iris readers.
They are protecting the hardware not just from theft, but from interference that could cause downtime.
Read our Article on: Windows Vulnerabilities Actively Exploited
The Miracle of Uptime
The next time you ask Siri a question at 3 AM or finish a work project on Google Docs, remember the invisible machinery humming away in a nondescript building somewhere.
Understanding exactly how data centers work 24/7 makes you appreciate that digital reliability isn’t magic—it’s a feat of engineering based on redundancy, immense power, and serious cooling.
Read More Technology and Software related Article




Just hopped onto jilibbcom the other day. Seems legit, decent selection of games. Worth a look-see jilibbcom.
Been grinding on Taya999com and things are going pretty good! Payouts are fast, and the customer support is responsive. Worth checking out taya999com.
Easy to log in, easy to play. That’s Taya99comlogin! If you’re looking for something straightforward, give it a shot. Good luck taya99comlogin.